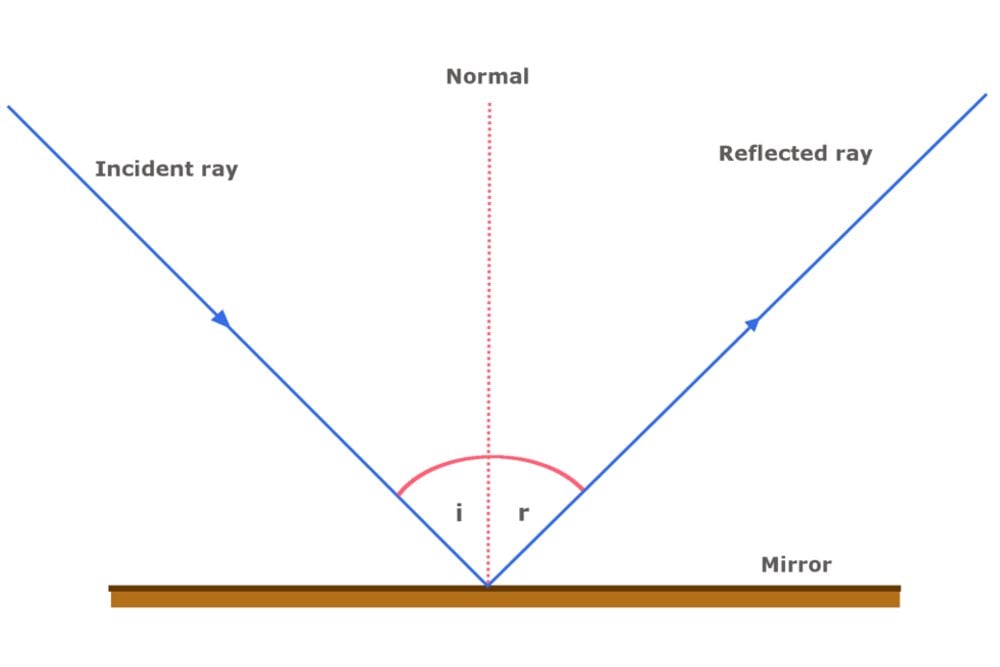
Laws of Reflection of Light MarkhasColon

The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as the reflected ray (labeled R in the diagram). At the point of incidence where the ray strikes the mirror, a line can be drawn perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. This line is known as a normal line (labeled N in the diagram).
Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu

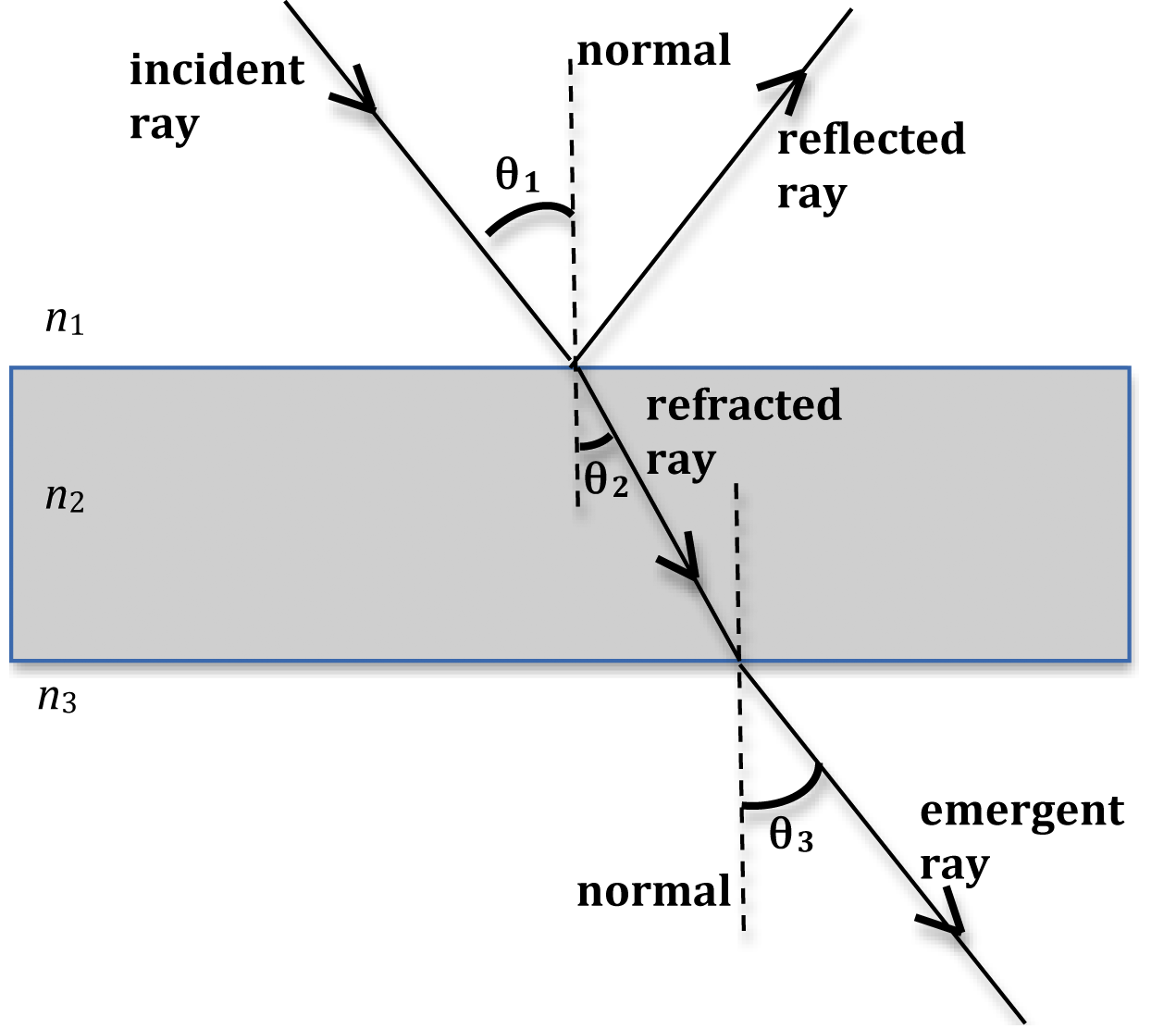
Figure 25.4.1 25.4. 1: (a) A ray of light crosses a boundary where the speed of light increases and the index of refraction decreases. That is, n2 < n1 n 2 < n 1. The ray bends away from the perpendicular. (b) The critical angle θc θ c is the one for which the angle of refraction is . (c) Total internal reflection occurs when the incident.
What Is The Law Of Reflection Definition And A Simple Explanation
What is EVIDENT? Today, many microscope manufacturers offer models that permit the user to alternate or simultaneously conduct investigations using both vertical and transmitted illumination. A typical microscope configured for both types of illumination is illustrated in Figure 1.
PHYSICS IS FUN REFLECTION OF LIGHT
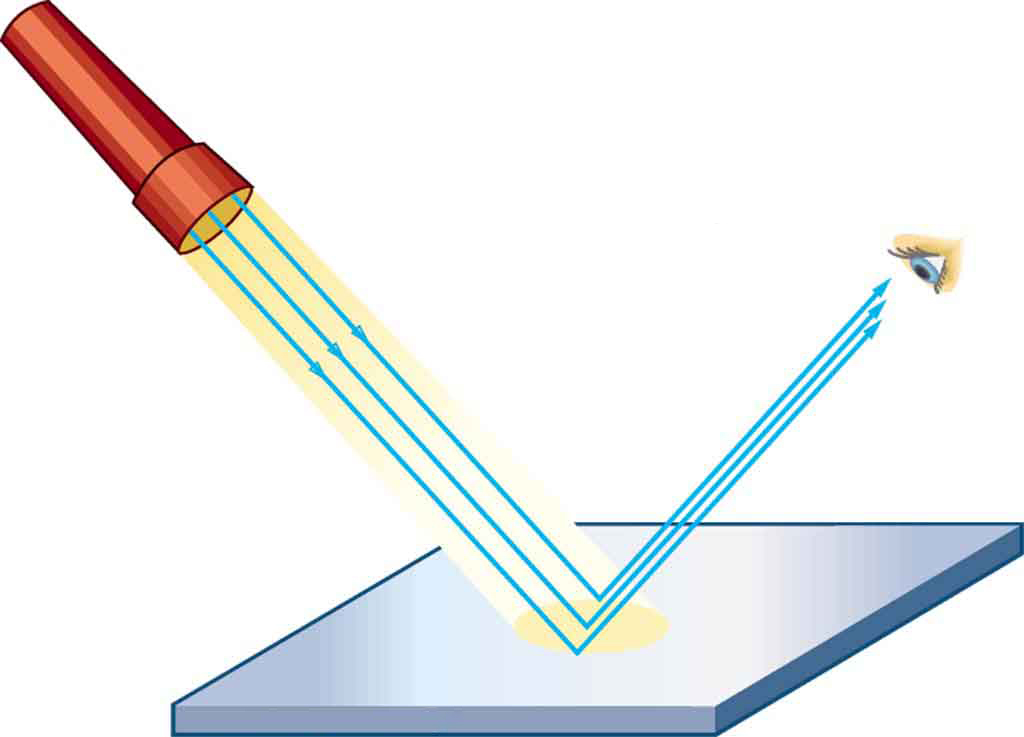
Figure 1.7 (a) When a sheet of paper is illuminated with many parallel incident rays, it can be seen at many different angles, because its surface is rough and diffuses the light. (b) A mirror illuminated by many parallel rays reflects them in only one direction, because its surface is very smooth. Only the observer at a particular angle sees the reflected light.
Lab 10 Reflection and Refraction
Article Reflection of light Resource Related topics & concepts Add to collection Reflection is when light bounces off an object. If the surface is smooth and shiny, like glass, water or polished metal, the light will reflect at the same angle as it hit the surface. This is called specular reflection. Topics Concepts Citizen science Teacher PLD
Example Of Reflection And Refraction
In a ray diagram, rays of light are drawn from the object to the mirror, along with the rays that reflect off the mirror. The image will be found where the reflected rays intersect. Note that the reflected rays obey the law of reflection.
CHAPTER 10 LIGHT REFLECTION AND REFRACTION(CBSE CLASS 10) DEX ACADEMY
(a) Light reaches the upper atmosphere of Earth by traveling through empty space directly from the source (the Sun). (b) This light can reach a person in one of two ways. It can travel through a medium, such as air or glass, and typically travels from one medium to another. It can also reflect from an object, such as a mirror.
Definition Diffuse Reflection Photokonnexion

Light - Reflection, Refraction, Physics: Light rays change direction when they reflect off a surface, move from one transparent medium into another, or travel through a medium whose composition is continuously changing. The law of reflection states that, on reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of the incident ray.
Reflection of Light Definition, Types, Laws & More Leverage Edu

According to wave-based theories, the light waves spread out from the source in all directions, and upon striking a mirror, are reflected at an angle determined by the angle at which the light arrives. The reflection process inverts each wave back-to-front, which is why a reverse image is observed. The shape of light waves depends upon the size.
Diagram Of A Light Ray Being Reflected By Diagram Free Transparent PNG Download PNGkey
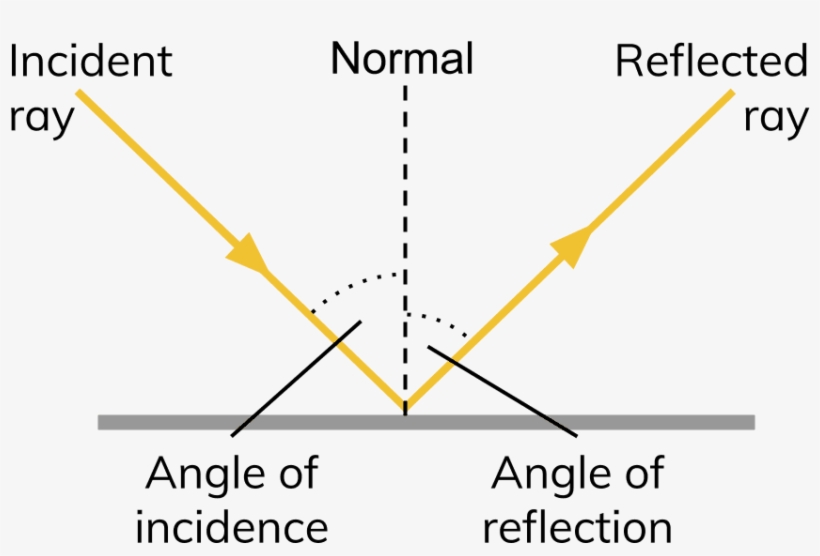
Diagram of specular reflection. In the diagram, a light ray PO strikes a vertical mirror at point O, and the reflected ray is OQ.. The reflected light is the combination of the backward radiation of all of the electrons. In metals, electrons with no binding energy are called free electrons. When these electrons oscillate with the incident.
Reflection and Refraction of Light & It's Applications hubpages
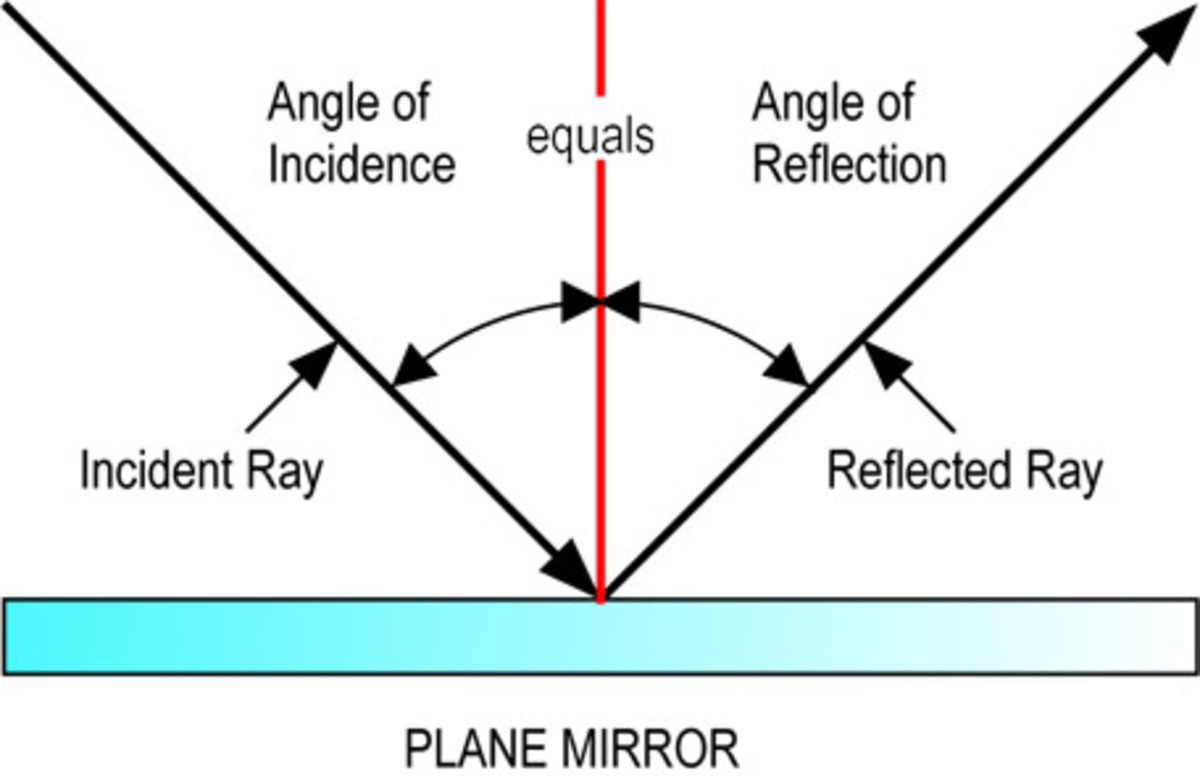
The diagrams show a light ray being reflected at a plane mirror. The law of reflection states that: angle of incidence = angle of reflection For example, if a light ray hits a surface at.
How Reflection Works in Physics
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ReflectionLaw-5946c6dd5f9b58d58a2f2efc.png)
To figure out where the image of this object is located, a ray diagram can be used. In a ray diagram, rays of light are drawn from the object to the mirror, along with the rays that reflect off the mirror. The image will be found where the reflected rays intersect. Note that the reflected rays obey the law of reflection.
Light Reflection Image & Photo (Free Trial) Bigstock

Reflected light microscopy is often referred to as incident light, epi-illumination, or metallurgical microscopy, and is the method of choice for fluorescence and for imaging specimens that remain opaque even when ground to a thickness of 30 micrometers.
Polarization by reflection of light Class Twelve Physics

The reflected light continues to travel in a straight line, but in a different direction.. Shown is a colour diagram of light bending as it refracts through material. The upper half of the diagram has a light grey background. This is labelled, "Material 1." The lower half has a darker grey background.
Reflection of light Concave mirrors, Light reflection, Mirror reflection

When you look at this page, too, you are seeing light reflected from it. Large telescopes use reflection to form an image of stars and other astronomical objects. The law of reflection is illustrated in Figure 25.4 , which also shows how the angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray strikes.
Specular and Diffusion ReflectionHow Light Reflects MooMooMath and Science
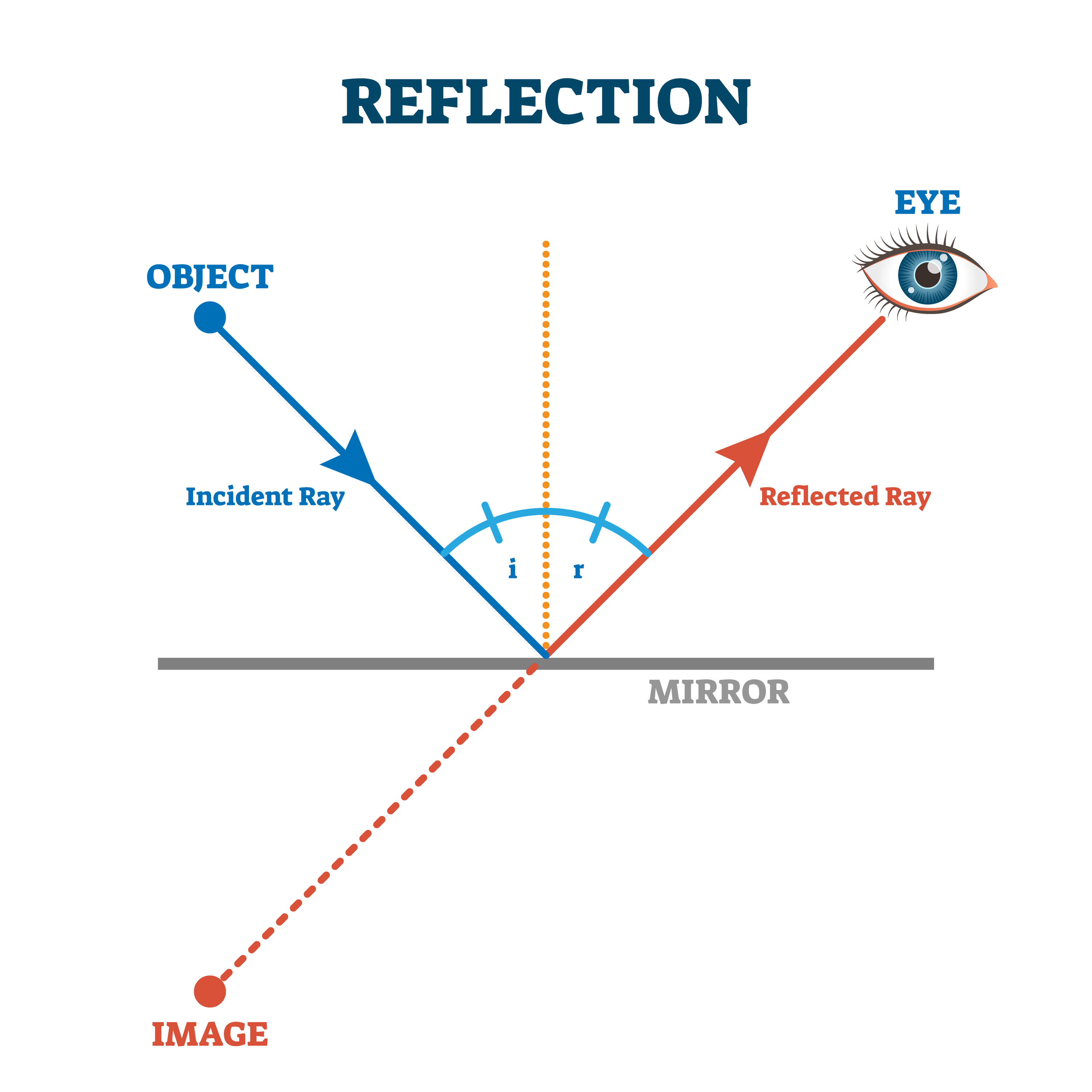
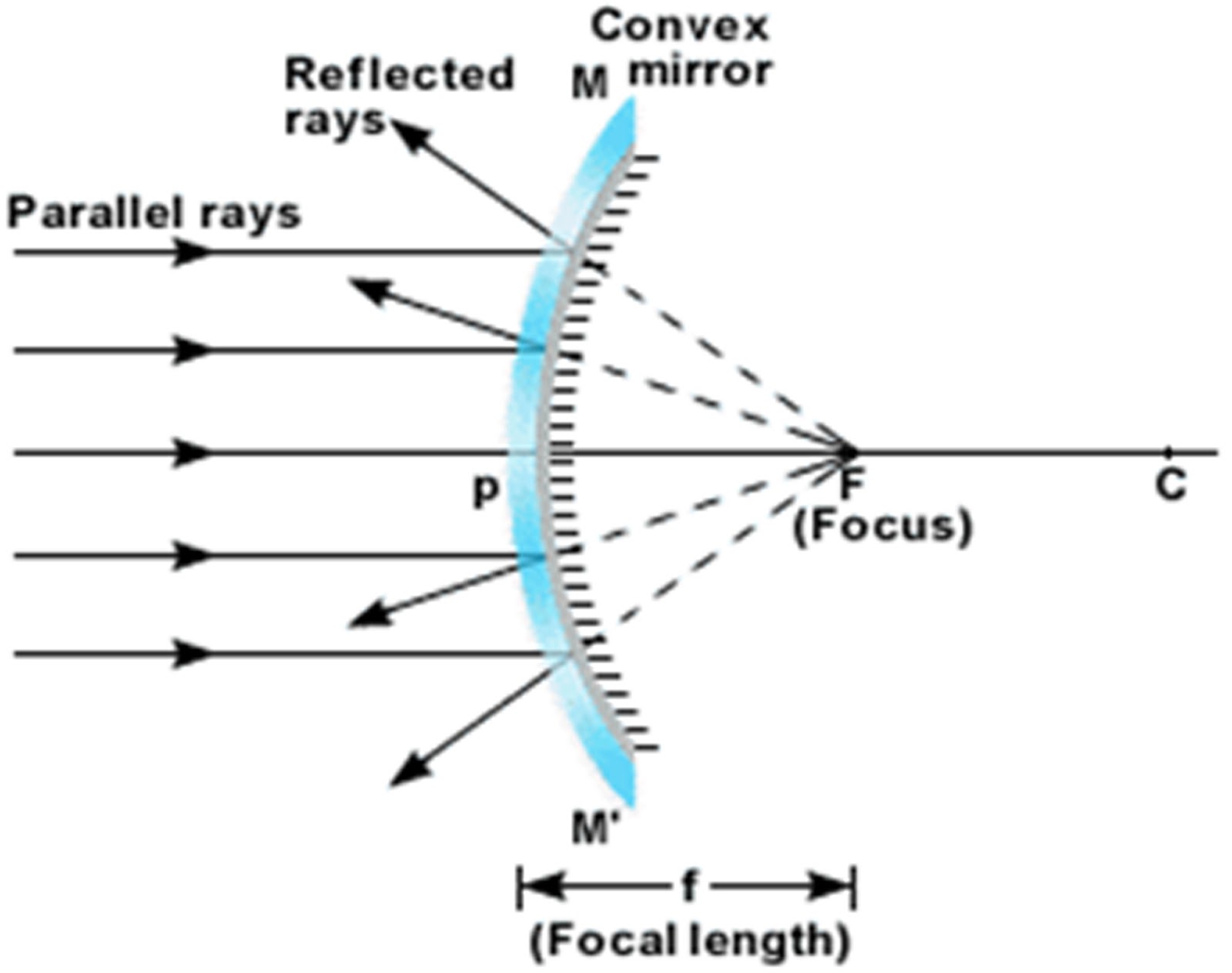
At the point where the light from the object converges, a replica, likeness or reproduction of the actual object is created. This replica is known as the image. Once the reflected light rays reach the image location, they begin to diverge. The point where all the reflected light rays converge is known as the image point.